( See also
NRPE for monitoring Windows )
The NRPE (Nagios Remote Plugin Executor) addon is designed to allow you to execute Nagios plugins on remote Linux/Unix machines. The main reason for doing this is to allow Nagios to monitor "local" resources (like CPU load, memory usage, etc.) on remote machines. Since these public resources are not usually exposed to external machines, an agent like NRPE must be installed on the remote Linux/Unix machines.
DESIGN OVERVIEW
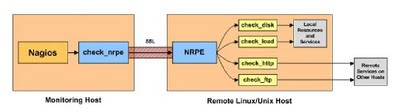
The NRPE addon consists of two pieces:
* The check_nrpe plugin, which resides on the local monitoring machine.
* The NRPE daemon, which runs on the remote Linux/Unix machine
When Nagios needs to monitor a resource of service from a remote Linux/Unix machine:
* Nagios will execute the check_nrpe plugin and tell it what service needs to be checked
*The check_nrpe plugin contacts the NRPE daemon on the remote host over an (optionally) SSL
protected connection.
*The NRPE daemon runs the appropriate Nagios plugin to check the service or resource.
*The results from the service check are passed from the NRPE daemon back to the check_nrpe
plugin, which then returns the check results to the Nagios process.
INSTALLATION
REMOTE HOST SETUP
1) Install nagios plugins
These instructions should be completed on the remote Linux/Unix host where the NRPE daemon to be installed .
i.Create a user account for nagios
/usr/sbin/useradd nagios
passwd nagios
ii. Install the Nagios Plugins .Download the source code tarball of the Nagios plugins (visit:
http://www.nagios.org/download
ii.Extract the Nagios plugins source code tarball.
tar xzf nagios-plugins-1.4.6.tar.gz
cd nagios-plugins-1.4.6 .
iv. Compile and install the plugins.
./configure
make
make install
v.The permissions on the plugin directory and the plugins will need to be fixed at this point,
chown nagios.nagios /usr/local/nagios
chown -R nagios.nagios /usr/local/nagios/libexec
vi. Install xinetd
sudo apt-get install xinetd
2) Install the NRPE daemon
i.Download the source code tarball of the NRPE addon.
(visit:
http://prdownloads.sourceforge.net/sourceforge/nagios/nrpe-2.12.tar.gz) .
ii.Extract the NRPE source code tarball.
tar xzf nrpe-2.8.tar.gz
cd nrpe-2.8
iii. Compile the NRPE addon.
./configure
make all
iv. Install the NRPE plugin , daemon, and sample daemon config file.
make install-plugin
make install-daemon
make install-daemon-config
v. Install the NRPE daemon as a service under xinetd.
make install-xinetd
vi. Edit the /etc/xinetd.d/nrpe file and add the IP address of the monitoring server to the
only_from directive.
only_from = 127.0.0.1
vii. Add the following entry for the NRPE daemon to the /etc/services file.
nrpe 5666/tcp # NRPE
viii. Restart the xinetd service.
service xinetd restart
3) Test the NRPE daemon locally.
Its time to see if things are working properly. Make sure the nrpe daemon is running under xinetd.
Check the command :
netstat -at | grep nrpe
The output out this command should show something like this:
tcp 0 0 *:nrpe *:* LISTEN
Next, check to make sure the NRPE daemon is functioning properly. To do this, run the check_nrpe plugin that was installed for testing purposes.
/
usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H localhost
You should get a string back that tells you what version of NRPE is installed, like this:
NRPE v2.8
So you finished the remote host part..Now you have to configure the monitoring host.








